Asian Pear Varieties and Nutritional Differences
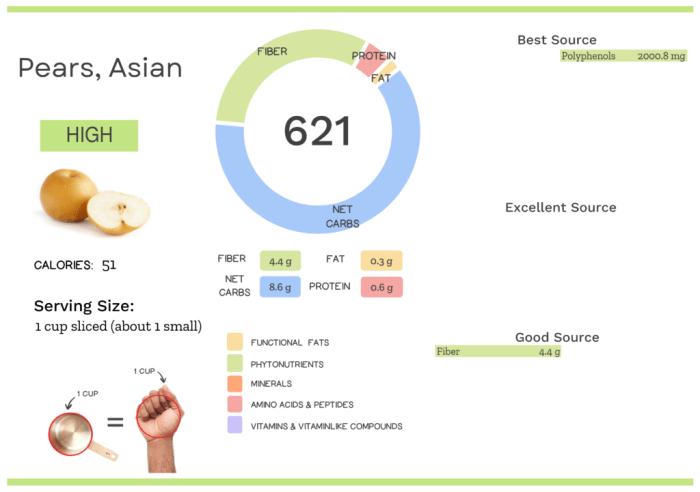
Asian pear nutrition facts – While the overall nutritional profile of Asian pears remains relatively consistent across varieties, subtle differences exist in their vitamin, mineral, and fiber content, impacting their taste, texture, and aroma. These variations are influenced by factors like growing conditions, ripeness, and specific cultivar characteristics. Understanding these nuances allows for a more informed selection based on individual preferences and dietary needs.
Nutritional Comparison of Asian Pear Varieties
The following table provides a comparative overview of the nutritional profiles of three common Asian pear varieties: Shinko, Hosui, and Nijisseiki. Note that precise values can vary based on growing conditions and testing methodologies. The data presented represents average values from multiple reputable sources.
| Variety | Vitamin C (mg/100g) | Fiber (g/100g) | Potassium (mg/100g) | Sugars (g/100g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shinko | 5-7 | 3-4 | 100-120 | 10-12 |
| Hosui | 6-8 | 2-3 | 110-130 | 13-15 |
| Nijisseiki | 4-6 | 2.5-3.5 | 90-110 | 9-11 |
Sensory Characteristics and Nutritional Relationships
The sensory characteristics of Asian pear varieties are closely linked to their nutritional composition. For instance, the higher sugar content in Hosui pears contributes to its sweeter taste compared to Nijisseiki. The slightly higher fiber content in Shinko pears might contribute to a slightly firmer texture. The variations in vitamin C content are less directly reflected in easily discernible sensory differences, but can still contribute to overall nutritional value.Shinko pears are known for their crisp, juicy texture and slightly tart flavor profile.
This balance of sweetness and acidity might be partly attributed to their moderate sugar and vitamin C levels. Hosui pears, on the other hand, are renowned for their exceptionally sweet and buttery taste and softer texture, which correlates with their higher sugar content and lower fiber content. Finally, Nijisseiki pears offer a balanced sweetness and crispness, falling between the Shinko and Hosui in terms of both taste and texture, reflecting their intermediate nutritional profile.
The aroma of each variety also differs subtly, with each possessing a unique fragrance that contributes to the overall sensory experience. While these subtle aroma differences are not directly quantifiable, they are an important part of the overall appreciation of these fruits.
Asian Pears in a Balanced Diet

Asian pears, with their sweet flavor and crisp texture, offer a delightful addition to a balanced diet. Their nutritional profile, rich in fiber and antioxidants, contributes to overall health and well-being, making them a versatile fruit for various meal occasions. Incorporating them strategically can enhance the nutritional value and flavor of your daily meals.
The versatility of Asian pears allows for seamless integration into various dietary patterns, contributing to a balanced intake of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Their naturally sweet taste reduces the need for added sugars, making them an ideal choice for those seeking healthier alternatives.
Sample Meal Plan Incorporating Asian Pears
This sample meal plan showcases the diverse ways Asian pears can be incorporated into a balanced diet throughout the day. The emphasis is on highlighting their versatility and maximizing their nutritional benefits.
Asian pears are a surprisingly nutritious snack, boasting a good source of fiber and vitamin C. However, if you’re curious about the nutritional breakdown of fast food options, you might want to check out the detailed nutrition facts about Wendy’s for comparison. This allows you to make informed choices about your overall dietary intake, contrasting the natural sweetness of the Asian pear with the often higher calorie and fat content of fast food.
Returning to Asian pears, their relatively low calorie count makes them a healthy alternative.
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with sliced Asian pear and a sprinkle of cinnamon. The fiber in both the oatmeal and pear promotes digestive health, while the cinnamon adds a touch of warmth and flavor.
- Lunch: A mixed green salad with grilled chicken or tofu, crumbled goat cheese, and thinly sliced Asian pears. The pears add a refreshing sweetness and contrasting texture to the salad, while the other ingredients provide protein and healthy fats.
- Dinner: Roasted pork tenderloin with a side of roasted root vegetables and a simple Asian pear chutney. The chutney provides a sweet and tangy counterpoint to the savory pork, adding depth of flavor and nutritional complexity.
- Snack: Sliced Asian pears with a small amount of almond butter. This combination provides a good source of fiber, healthy fats, and protein, offering sustained energy and satisfaction.
Creative Ways to Incorporate Asian Pears into Dishes
Beyond the basic snack or addition to salads, Asian pears lend themselves to creative culinary applications, enhancing both the taste and nutritional profile of a wide range of dishes.
- Salads: Their crisp texture and sweet flavor make them an excellent addition to various salads, offering a refreshing contrast to savory ingredients like grilled chicken, nuts, and cheeses. A pear and walnut salad with a light vinaigrette is a particularly appealing option.
- Desserts: Asian pears can be poached, baked, or used in crisps and cobblers. Their natural sweetness reduces the need for excessive added sugar, creating healthier dessert options. An Asian pear and ginger crumble is a delicious and relatively healthy dessert.
- Main Courses: Thinly sliced Asian pears can be incorporated into savory dishes such as pork or duck roasts, adding a unique sweetness and contrasting texture. Their juice can also be used in glazes or sauces to add a touch of sweetness and depth of flavor.
Asian Pears as a Healthy Snack Alternative
Often, we reach for less nutritious snacks when hunger strikes. Asian pears offer a delicious and healthy alternative to many processed snacks.
- Instead of reaching for a sugary candy bar, a sliced Asian pear provides natural sweetness and fiber, promoting satiety and preventing energy crashes. The fiber content contributes to a feeling of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake.
- As a replacement for chips or other salty snacks, an Asian pear provides a refreshing and naturally sweet alternative. The crunch satisfies the craving for texture without the excess sodium and unhealthy fats.
- Compared to processed fruit snacks, which often contain added sugars and preservatives, an Asian pear offers a wholesome and nutrient-rich snack choice. Its natural sugars provide energy without the negative health impacts associated with refined sugars.
Potential Allergic Reactions and Considerations: Asian Pear Nutrition Facts
While Asian pears are generally well-tolerated, allergic reactions are possible, though relatively uncommon compared to other fruits like apples or peaches. These reactions are typically caused by proteins found within the fruit, and their severity can range from mild to severe. Understanding potential reactions and taking appropriate precautions is crucial for individuals with known allergies or sensitivities.Allergic reactions to Asian pears can manifest in various ways.
Mild symptoms might include itching in the mouth or throat, mild swelling of the lips or tongue, or a skin rash. More severe reactions, though less frequent, can involve difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or face (angioedema), and even anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention. These severe reactions are often characterized by a rapid onset and can quickly escalate, making prompt treatment essential.
Allergen Cross-Reactivity
Cross-reactivity is a significant consideration for individuals with allergies to other fruits, particularly those in the Rosaceae family (rose family), which includes apples, pears, peaches, cherries, and plums. People with known allergies to these fruits have a higher likelihood of experiencing a reaction to Asian pears due to the presence of similar proteins that can trigger an allergic response.
This shared allergenicity means that careful avoidance of related fruits might be necessary for individuals with a history of such allergies. For example, someone with a known apple allergy might experience a similar reaction to an Asian pear, necessitating caution. A doctor or allergist can provide personalized advice and testing to determine the level of risk.
Precautions for Individuals with Dietary Restrictions or Allergies
Individuals with known fruit allergies, particularly those within the Rosaceae family, should exercise caution when consuming Asian pears for the first time. It’s advisable to start with a small amount to observe for any reactions. Having antihistamines readily available is also prudent, especially for individuals with a history of mild to moderate allergic reactions. For those with severe allergies, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen) is crucial and potentially life-saving.
Consulting an allergist or doctor before introducing Asian pears into the diet is highly recommended, particularly for individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions to other foods. They can conduct allergy testing to assess the level of risk and provide tailored guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Asian Pear Allergies and Their Management, Asian pear nutrition facts
The following points address common concerns surrounding Asian pear allergies:
Individuals often inquire about the symptoms of an Asian pear allergy. Symptoms can vary significantly in severity and presentation, ranging from mild oral itching to life-threatening anaphylaxis. Mild reactions might include oral itching, tingling, or swelling, while severe reactions could involve difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, and a sudden drop in blood pressure.
Another common question involves the best approach for managing an Asian pear allergy. Management strategies depend on the severity of the reaction. Mild reactions may only require antihistamines, while severe reactions necessitate immediate medical attention and the use of epinephrine. Allergy testing can help determine the severity of the allergy and guide management strategies.
Many people wonder about the possibility of outgrowing an Asian pear allergy. While some allergies may lessen in severity or even disappear over time, particularly those developed during childhood, this is not always the case. Regular monitoring and consultation with an allergist are crucial for determining the progression or persistence of the allergy.
FAQ Section
Are Asian pears good for weight loss?
Their relatively low calorie count and high fiber content can contribute to feelings of fullness, potentially aiding in weight management. However, weight loss depends on overall dietary habits and caloric intake.
Can I eat Asian pears if I have diabetes?
While Asian pears contain natural sugars, their moderate glycemic index (GI) generally makes them a suitable choice for people with diabetes, but portion control is recommended and monitoring blood sugar levels is essential.
How should I store Asian pears to maintain their freshness?
Store Asian pears at room temperature until ripe. Once ripe, refrigerate them to slow down the ripening process and prolong their shelf life.
What are the signs of an Asian pear allergy?
Symptoms can range from mild (itching, rash) to severe (anaphylaxis). Common symptoms include oral allergy syndrome, skin reactions, and gastrointestinal distress. If you experience any allergic reactions, seek medical attention immediately.
















0